Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly changing the gaming industry. In addition to increasing efficiency in game development and improving accessibility, the biggest impact of generative AI is likely to be on in-game content.
Games are complex and a huge entertainment market. Roughly 3.2 billion players generated $184.4 billion in annual revenue in 2022, according to Newzoo, a leader in video games and gamer data. Given the size, the gaming market is ripe for disruption by generative AI.
The cost of creating games is a major limiting factor. Roughly 40% of the total cost goes toward creating art assets, underscoring the significance of leveraging generative AI tools and services. Particularly, the remarkable capability of the technology to assimilate patterns, structure data, and swiftly generate fresh 3D content, all while significantly reducing costs. According to PwC, the value of integrating generative AI into gaming could be worth up to $321 billion by 2026.
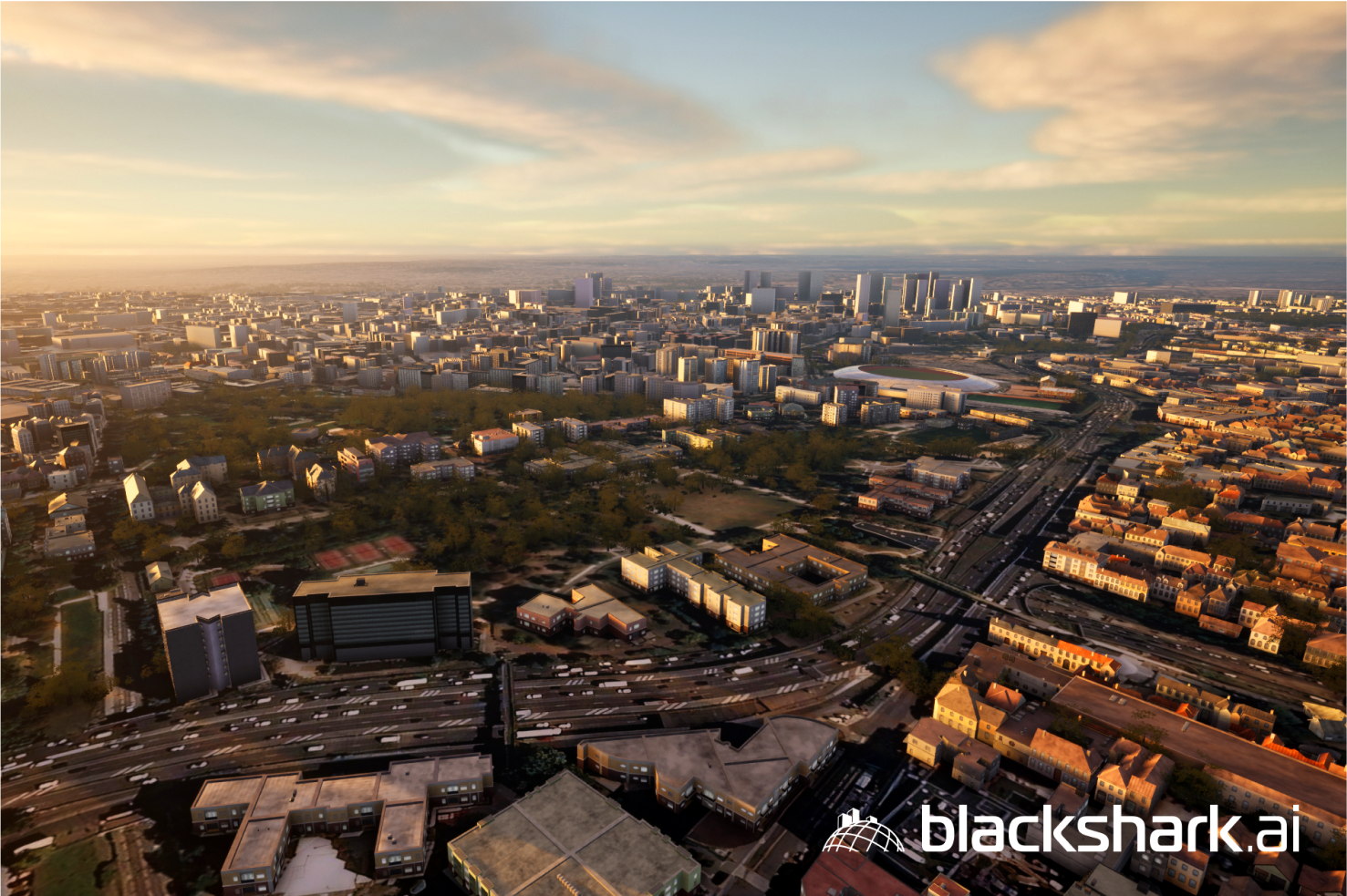
Drawing parallels with prominent online platforms such as Spotify (audio), Instagram (photos), and YouTube (videos) allows us to envision the impending revolution in in-game content production due to generative AI. Just as these platforms revolutionized their respective industries by allowing users to generate content, generative AI promises to do the same within the gaming landscape. Comparing Red Dead Redemption 2, one of the most detailed games, with Microsoft Flight Simulator offers an idea of how generative AI has transformed gaming. The former costs $500 million and took almost eight years to build, while the latter – a far more detailed and enormous game – was built by training an AI model to create a 3D version of the earth from 2D satellite images. Blackshark.ai, Microsoft’s partner for the game, used its AI technology to display the entire 197 million square miles of Earth’s surface in 3D – with over 1.5 billion photorealistic buildings – giving users an unprecedented immersive 3D flight experience and the largest open world in the history of video games.

In addition to game studios, the potential transformation of the gaming ecosystem by generative AI opens opportunities for generative AI start-ups as well. Respeecher, for instance, specializes in AI voice augmentation technology. Developers can use Respeecher’s Voice Marketplace to create custom voice content that fits the tone and style of their game, resulting in a more immersive and engaging experience for players. Expanding beyond voice augmentation, start-ups like Stability AI have harnessed generative AI to expedite the creation of visually stunning images. Traditionally, developing high-quality graphics for games was a time-consuming process that could take weeks or even months. However, with Stability AI’s generative algorithms, game developers can generate captivating images within minutes or hours. Another noteworthy start-up in this space is California-based Scenario. Recognizing that each game possesses a distinct visual aesthetic, Scenario offers game developers the ability to create image generators specifically tailored to their game’s unique style. Similarly, Rosebud AI also offers AI-generated game assets for game development.
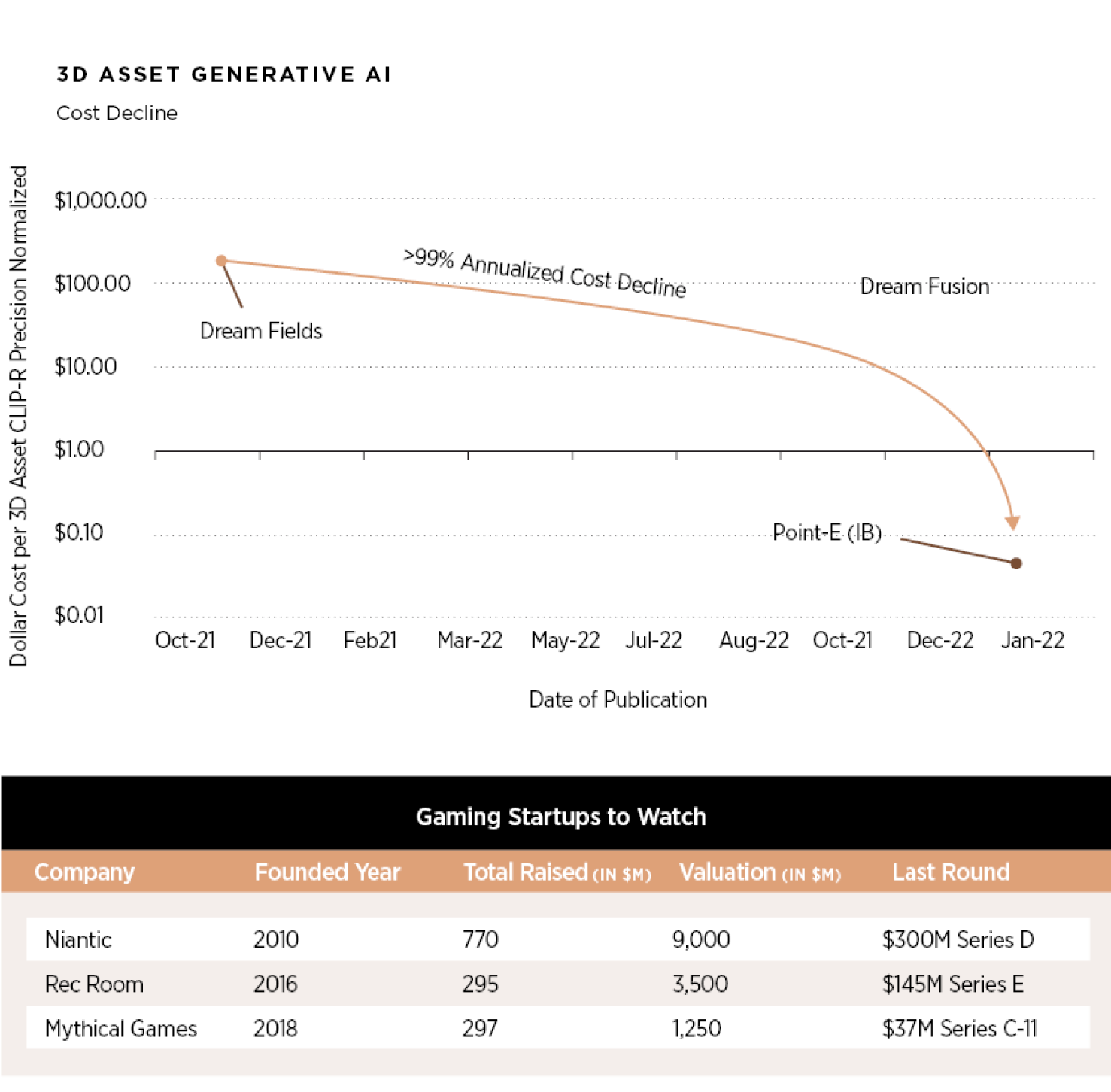
A generative AI-enabled drop-in time and the cost of the in-game user-generated content are other factors propelling the adoption of generative AI. According to ARK Invest, text-to-3D model costs have plummeted by almost 99% in the past year. Some developers have even witnessed a 120:1 reduction in their time to generate concept art for a single image within a game.
However, the current models still produce single, unified outputs, requiring manual fragmentation by game artists and developers to create dynamic game assets. Soon, game engines are expected to integrate with text-to-3D models, enabling creators and developers to generate and edit assets seamlessly within their ecosystem. These advancements in text-to-3D generative AI mark a crucial turning point for the gaming industry, hastening the widespread adoption of generative AI in gaming.
Unity, a leading software company used by 70% of mobile games, is strategically integrating generative AI into games. According to Unity CEO John Riccitiello, it has the potential to drive 10X growth in the gaming industry. Looking ahead, we expect generative AI to permeate multiple aspects of game development and not just in-game content. By doing so, generative AI start-ups can transform game development and expand the frontier.
| GENERATIVE AI REGULATION: A DELICATE BALANCING ACT
The arrival of new technologies typically stirs a mix of excitement as well as anxiety. However, the degree of concern surrounding the implications of artificial intelligence (AI) advancements is significant. The rapid progress of AI has not only prompted regulatory scrutiny but also a comprehensive evaluation of its potential impact.
Regulators worldwide are actively working toward the regulation of generative AI. Notably, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman recently urged members of Congress in the US to implement AI regulations. Altman, actively involved in a robust lobbying campaign, has sought discussions with congressional leaders from both political parties to emphasize the significance of regulating AI. In a significant development, the European Parliament’s committee of lawmakers approved the EU’s AI Act in May, bringing it closer to becoming a law. This regulation adopts a risk-based approach and includes specific requirements for developers of “foundation models” like ChatGPT, ensuring compliance with copyright laws in their training data. China is also poised to present a draft of its AI law to the country’s lawmakers for review later this year. Furthermore, the Canadian parliament is also considering its own hotly contested Artificial Intelligence and Data Act.
The generative AI landscape is rapidly evolving, making it challenging to craft specific and comprehensive regulations that can keep pace with the technology’s rapid advancements. Instead of rigid regulations, a more suitable approach would be to establish guardrails that foster responsible development and deployment of generative AI.

"The generative AI landscape is rapidly evolving, making it challenging to craft specific and comprehensive regulations that can keep pace with the technology’s rapid advancements"
While the advocates of heavy regulation argue that there is a need for a separate regulatory entity to oversee generative AI, it is important to recognize that the legal framework surrounding AI already exists, albeit in a broader context. Laws such as intellectual property rights, privacy regulations, and anti-discrimination laws can effectively address potential issues related to generative AI without stifling its progress. US Senator Ron Wyden of Oregon is working on the Algorithmic Accountability Act, a law that would require testing of high-risk AI before deployment.
AI is already subject to significant regulation, including data protection laws like the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation and the US’s Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. These regulations play a crucial role in safeguarding personal information and ensuring accountability.
It is also worth noting that generative AI is already being utilized in heavily regulated sectors such as healthcare and finance, highlighting the existing framework of regulations in these critical domains. Moving forward, the regulation of specific sectors within the AI landscape will remain vital. As AI continues to advance and permeate various industries, targeted regulations tailored to each sector’s unique challenges and requirements will play a crucial role in ensuring ethical and responsible AI deployment. Such sector-specific regulations can address concerns related to privacy, security, transparency, bias, and accountability, among other important considerations.
However, lawmakers must remain wary of the lobbying efforts exerted by influential Big Tech companies such as Alphabet, Microsoft, and OpenAI. These companies possess significant resources and political influence, which can sway policy and regulatory decisions in their favor. While their contributions to innovation and technological advancement are undeniable, lawmakers need to maintain an independent and objective perspective. By critically evaluating the lobbying activities of these companies, lawmakers can ensure that regulations are formulated in the best interest of the public and not unduly influenced by private agendas.
At the heart of the ongoing debate surrounding the regulation of AI lies the fundamental challenge of striking the right balance between mitigating risks and fostering its continued growth. This intricate task demands an approach that involves comprehensive deliberation and engagement from various stakeholders, rather than solely relying on technologists to determine the course of action.
| ENTERPRISE-GRADE LLMS: THE NEXT BIG THING IN GENERATIVE AI
Contextual AI, a California-based generative AI start-up, raised a $20 million seed funding round from investors including Bain Capital Ventures, Lightspeed, Greycroft, and SV Angel. The company is name-building large language models (LLMs) that are purpose-built for enterprises.
We believe such LLMs are going to play a vital role in meeting the demands of enterprise-grade AI due to the limitations of current LLMs and the specific requirements of businesses in terms of accuracy, reliability, compliance, and data privacy. While LLMs like OpenAI’s GPT-4 are powerful tools, their training on general internet data often leads to inaccuracies when confronted with specific fact-based questions, making them less attractive to enterprises, particularly the ones with strict compliance and governance requirements. However, companies like Contextual AI offer a solution by building platforms that enable businesses to develop, train, and deploy their customized LLMs, addressing compliance and privacy concerns while delivering significantly improved performance.

Contextual AI’s platform focuses on grounding LLMs in underlying data sources, allowing them to generate factual responses more reliably. By incorporating external sources such as files and webpages, Contextual AI’s retrieval augmented generation (RAG) technique enhances the performance of LLMs, providing context-aware responses. This approach not only ensures better accuracy but also eliminates the need for extensive retraining or fine-tuning when adding data sources—a significant advantage over conventional LLMs. The typical enterprise environment deals with vast amounts of unstructured data generated through various channels like text, images, and video. While conventional LLMs excel in comprehending and extracting insights from this unstructured data, their size, and their resource requirements pose implementation challenges for many enterprises. Contextual AI’s platforms offer a solution by enabling businesses to build and deploy smaller, yet equally performant, LLMs. These models not only provide faster processing and lower latency but also alleviate the burden of infrastructure costs.
| STARTUPS IN AI VALUE CHAIN RIPE FOR ACQUISITION
In June, Databricks agreed to acquire artificial intelligence (AI) startup MosaicML in a mostly stock deal valued at $1.3 billion. The deal comes at a time when AI is dominating the tech industry, with rapid CapitalAI thrusts coming from big tech, including Alphabet’s Google and Microsoft, and venture capital investors pouring billions into funding AI startups.
The demand for generative AI is skyrocketing, and tech giants are scrambling to secure their positions in this lucrative market. Accordingly, start-ups across the generative AI value chain are becoming prime acquisition targets, drawing the attention of industry leaders seeking to capitalize on their value and innovation. In addition to Databricks, Thomson Reuters also agreed to acquire legal AI assistant Casetext for $650 million. While a majority of acquisitions are happening in the application layer, we also see AI chip start-ups as key acquisition targets for hardware incumbents. With the AI chips market being highly consolidated, market leaders such as NVIDIA and AMD might pursue inorganic strategies for growth by acquiring US-based AI-chips startups such as Sambanova Systems, Groq, Cerebras Systems, Graphcore, etc.
"Start-ups across the generative AI value chain are becoming prime acquisition targets, drawing the attention of industry leaders seeking to capitalize on their value and innovation"
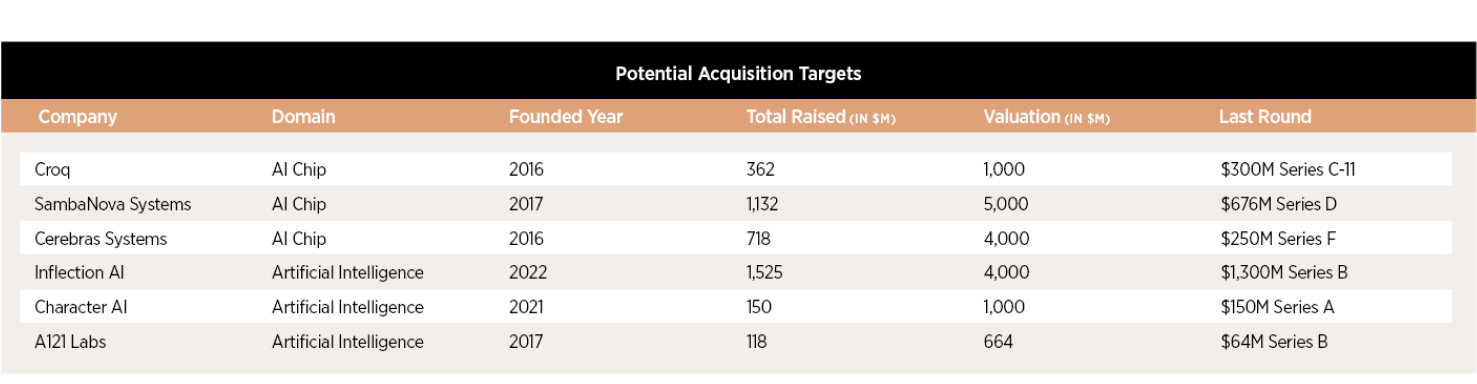
For reference, NVIDIA currently has an 84% market share in GPU, per data from Jon Peddie Research. Government regulations, such as the CHIPS for America Act and the FABS Act, are also likely to play a key role in the M&A frenzy. Restrictions on AI chip trade with China have prompted industry players to focus on opportunities within the US, increasing the allure of American AI chip start-ups as attractive acquisition targets. Moreover, businesses are strategically pursuing early-stage AI startups for acquisition, incorporating the startup’s AI technologies into their operations. This approach allows such businesses to maintain control over their data and avoid sensitive data sharing with third-party AI entities. For instance, Nextiva acquired Simplify360 post series A round, Amazon acquired Snackable AI post seed VC round, and BioNTech acquired InstaDeep post series B round. In line with the trend, early-stage generative AI startups such as Inflection AI, Character AI, and AI21 Labs are potential targets for acquisition in the near future.

Manhattan Venture Partners
MVP is a one-stop principal investor and advisory solution to private venture-backed companies.
mvp.vc





